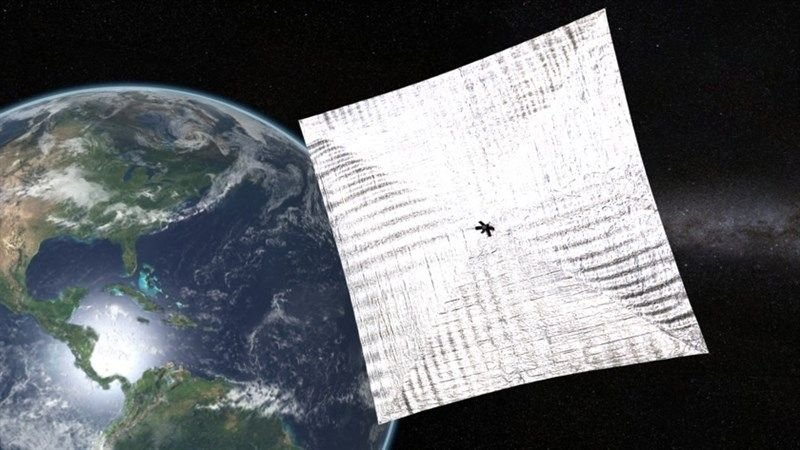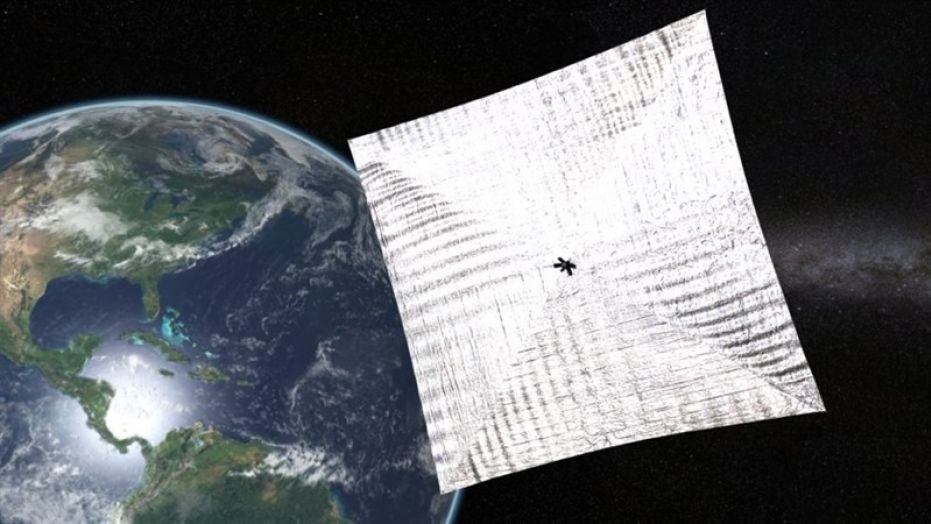
LightSail 2, set to release no earlier than June 13, 2018, will show up to observers on the ground as it orbits Earth for a month or more.(Credit: The Planetary Society)
A new solar-sailing spacecraft will be a call to all (future) residents of interplanetary craft. The Planetary Society’s LightSail 2 spacecraft will be a test bed for future missions wishing to utilize solar sails– consisting of NASA’s proposed cubesat, the Near-EarthAsteroid Scout (NEA Scout).
LightSail2 will launch no earlier than June 13 from the Kennedy Space Center near Orlando, Florida, utilizing Space X’s new and effective FalconHeavy rocket. The spacecraft’s supreme location will be medium-Earth orbit of about 725 kilometers (450 miles)– approximately double the elevation of the InternationalSpace Station.
The objective’s supreme objective is to check out “flight by light,” as The Planetary Society calls it– solar cruising in area. This kind of propulsion utilizes the mild push of photons streaming from the sun to move the spacecraft around. The biggest advantage is that the spacecraft does not need to bring fuel with it. On a little satellite like a cubesat, stated Bruce Betts, primary researcher of The Planetary Society, every gram of weight counts. [The Evolution of Solar Sails in Photos]
“We’ve been waiting for a launch where we could get to a higher altitude [above Earth], where solar pressure will dominate over the atmospheric drag,”Betts informedSpace com.
MoreFromSpace com
“We actually will be trying to do controlled solar sailing … every half an [Earth] orbit, we will be pushed by the sunlight, and for the other half of the orbit, we will be edge-on to the sunlight,” included Betts, who is likewise The Planetary Society’s director of science and innovation.
Improvements from LightSail 1
ThePlanetary Society’s LightSail 1 released on May 20, 2015, in addition to the Air Force’s supersecret X-37 B area aircraft. It endured for simply under a month in low Earth orbit. While it satisfied its significant mission goal of releasing the sail, the test flight had a number of problems along the method.
Just 2 days after launch, a software application problem postponed strategies to release the solar sail up until June 7. The spacecraft sent an image June 9 revealing that the sail unfurled effectively, satisfying its main mission goal. But then, more issues developed.
“Before engineers could get a picture from the opposite-side cameras, LightSail’s radio began transmitting a continuous, nonsensical signal, and the spacecraft stopped responding to commands,” stated the Planetary Society’s Jason Davis in a post on June 15,2015 The spacecraft likewise stopped transferring on June 10, quickly prior to it went into the environment as initially prepared.
“We learned a lot from LightSail 1,”Betts stated. “It taught us a lot about the spacecraft, and after the various issues, we made a lot of improvements.”
Some of the crucial enhancements will assistance LightSail 2 make more effective usage of the particles coming its method. The most significant hardware distinction is a momentum wheel, or a quickly spinning wheel that assists LightSail 2 keep position in area. Its mindset decision and control software application is various from LightSail 1’s devices. The cams were likewise updated to send higher-quality pictures of the sails.
Other enhancements were planned to make the spacecraft more robust. Instead of “waiting for reboots to sometime, magically happen,” Betts stated, there are timers on board with automated settings to reboot procedures, or, at worst, to reboot the whole spacecraft in case of difficulty. More info will be consisted of in the radio signal to provide controllers info about the spacecraft’s health status. Engineers likewise included reflectors to make the position of LightSail 2 much easier to track from the ground.
Interplanetary craft
A few other spacecraft have actually effectively checked out solar cruising in area. The most significant example is the Japanese Ikaros(InterplanetaryKite- craft Accelerated by Radiation Of the Sun), which effectively took a trip utilizing a solar sail in 2010 throughout Japan’s Akatsuki objective toVenus It’s the only spacecraft that utilizes that technique to move up until now in deep area– in 2012, Ikaros got the Guinness World Record as the very first solar sail spacecraft in between worlds. [Are Solar Sails the Future of Space Travel?]
NASA likewise released a solar sail on the NanoSail-D2 in low Earth orbit in 2010 too; that objective focused more on the sail’s implementation, and how the sail acted in low Earth orbit. (The company prepared another solar-sailing objective called Sunjammer, however it was canceled prior to launch.)
This implies LightSail 2 will include extremely required, real-world info about how solar sails act in area. Its group touches with another solar sail speculative group too: the NEA Scout group, which will utilize a solar sail to zip an asteroid. “They are planning on using a solar sail with similar type design and characteristics to LightSail 2,” Betts stated.
NEA Scout is set up to sign up with a lots other small missions aboard the Orion’s Exploration Mission -1, which will likewise be the very first test flight of NASA’s SpaceLaunch System and is presently set up for no earlier than2019 NEA Scout is anticipated to fly past an asteroid called 1991 VG, although the choice to zip the asteroid hasn’t been settled yet.
Solar cruising is a possible propulsion technique for distant-future interstellar missions since fuel does not have to be continued board. NASA has actually experimented with numerous mission-concept concepts. Similarly, the independently moneyed Breakthrough Starshot effort prepares to utilize a laser in mix with a sailto send out a small probe to Earth’s nearby galaxy, Alpha Centauri.
Original post on Space com.
.