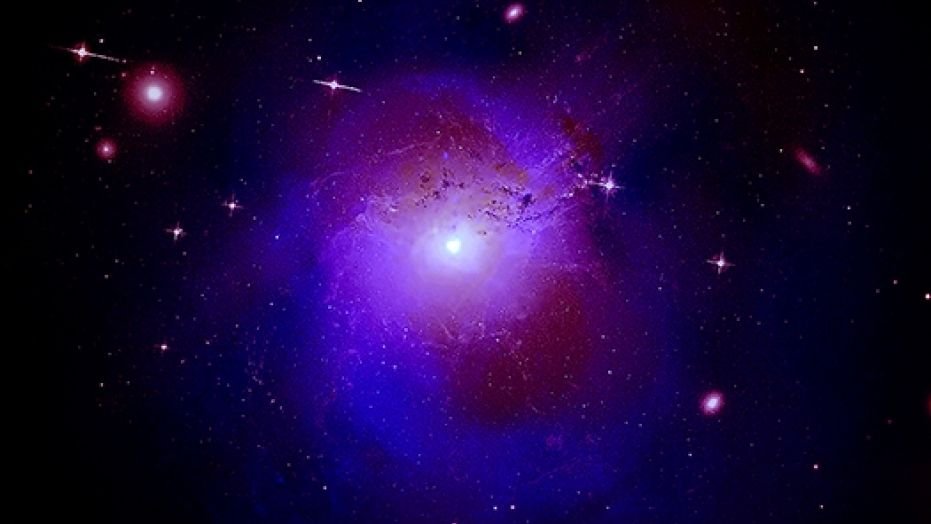
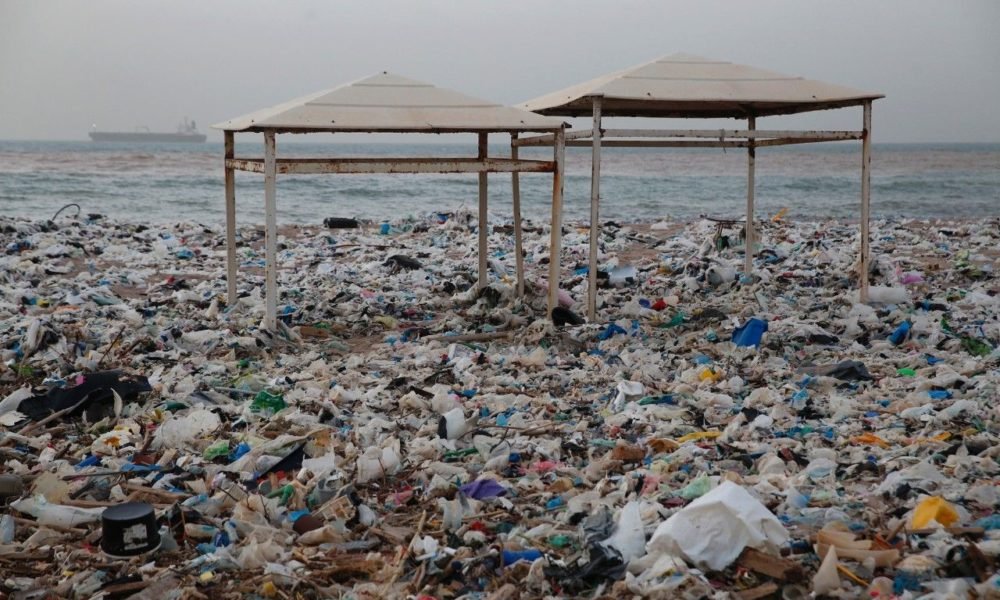
A composite image of X-ray and optical observations of the Perseus galaxy cluster. This image includes X-ray information from the Chandra X-ray Observatory (blue) of the Perseus galaxy cluster. The observations have actually been integrated with optical information from the Hubble area telescope (pink) and radio-emission information from the Very Large Array (red) in NewMexico If these findings are validated with future observations, it would indicate a significant advance in understanding the nature of dark matter, scientists stated in a declaration.( NASA/ESA/CXO/OxfordUniversity/ NRAO/AUI/Universityof Montreal)
X-ray light from the Perseus cluster of galaxies may lastly reveal the real nature of one of the most mysterious compounds in the universes: dark matter.
Darkmatter is an unusual product that does not give off light or energy, yet is believed to comprise about 85 percent of the matter in deep space. Researchers utilize imaginative and indirect observations to deduce dark matter’s existence, however it stays tough to select strong proof of the compound’s presence. Thanks to installing observations by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, a Japanese- led X-ray telescope called Hitomi and the European Space Agency’s (ESA) XMM-Newton, researchers may be on the edge of a groundbreaking discovery about the mysterious product, scientists stated in a declaration from the Chandra X-RayCenter in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
The topic of research study is the Perseus cluster, a dirty area of galaxies congregated 250 million light-years fromEarth Scientists price quote that the Perseus cluster is 11.6 million light-years throughout which it may include a massive 660 trillion times the mass of the sun.
In2014, an uncommon spike of strength in X-ray wavelengths captured the attention of scientists utilizing the XMM-Newton area observatory. The waves were coming from heated gas in the Perseus stellar cluster, near the. Researchers likewise discovered that this very same wavelength of radiation, called an emission line, was originating from 73 other galaxy clusters, inning accordance with the declaration.
MoreFromSpace com
That2014 observation revealed radiation originating with 3.5 kiloelectron volts (keV) of energy, and a brand-new analysis identified an absorption of X-rays– likewise at 3.5 keV– surrounding a supermassive great void at the center of the Perseus cluster. Researchers have actually discovered it almost difficult to describe why that specific wavelength is being produced and taken in, and since previously-seen huge items do not appear to reveal hints about the wavelength emission, they recommended dark matter might be the cause.
“We expect that this result will either be hugely important or a total dud,” stated Joseph Conlon of the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, lead author of the current research study. “I don’t think there is a halfway point when you are looking for answers to one of the biggest questions in science.” The brand-new paperdescribing the group’s outcomes was released in the journal Physical Review D onDec 19.
Ifdark matter triggered the irregular emission and absorption lines at that wavelength– both emitting and taking in X-rays within the collection of galaxies– more observation might teach scientists more about the mysterious compound, the researchers stated.
Fortunately, effective X-ray telescopes presently being established will let researchers make more-precise observations of these remarkable X-ray emission lines.
Original short article on Space com.
.