As financial activity resumes in China following the very first wave of the coronavirus pandemic, levels of the air toxin nitrogen dioxide (NO2) are increasing to traditional requirements for the very first time this year.
Accordingto NASA’s Earth Observatory reports, in February of 2020 researchers utilizing NASA and European satellites recognized there was a considerable decrease in NO2 over the nation after COVID-19 shutdown guidelines worked.
As CORONAVIRUS LOCKDOWN DECREASES CONTAMINATION IN NEPAL, MOUNT EVEREST VISIBLE FROM OVER 120 MILES AWAY
With the conclusion of strict health requireds, simply 3 months later on researchers saw their expected rebound.
NO2 is a poisonous gas discharged mostly through the burning of gas, coal, and diesel fuel by automobile, power plants, and commercial centers.
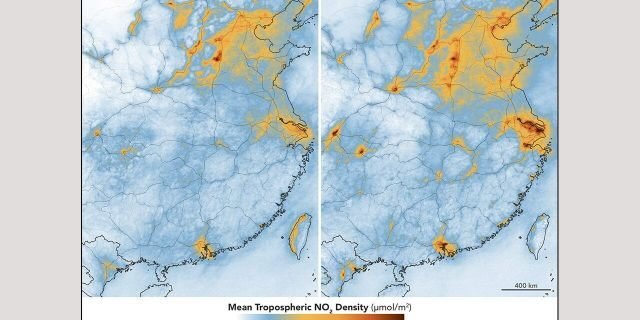
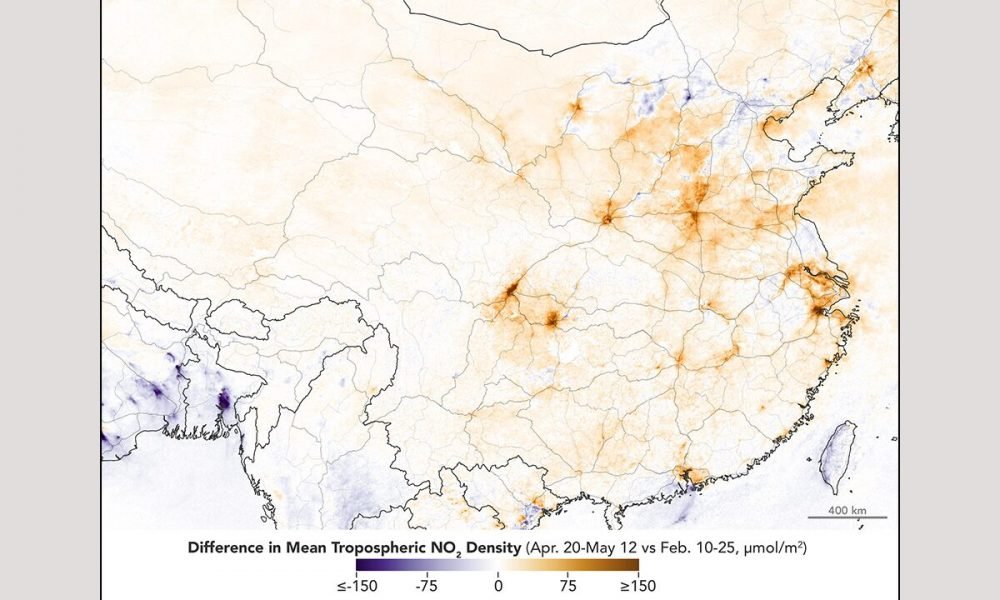
The maps on this page program levels of nitrogen dioxide in the troposphere (the most affordable layer of the environment) overChina The maps above program NO2 levels in main and eastern parts of the nation from February 10–25(throughout the quarantine) and April 20 to May 12 (after constraints were raised). (NASA)
When nitrogen dioxide is more detailed to the Earth’s surface area, it can develop into ozone that reduces air quality and makes breathing conditions unhealthy. When greater in our environment, NO2 can form acid rain.
Researchers at NASA’s GoddardSpace Flight Center’s AtmosphericChemistry and Dynamics Laboratory have actually kept an eye on NO2 along with basic worldwide air quality for numerous years.
Data gathered by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) on the European Space Agency’s CopernicusSentinel -5 P satellite significant noteworthy modifications in levels of nitrogen dioxide in the troposphere over China throughout durations throughout and after shutdowns.
TheOzone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA’s Aura satellite — which offers lower spatial resolution, however a longer information record– has actually made similar measurements because the early 2000 s.
Interestingly enough, previous research study has actually exposed that air contamination in China generally reduces throughout New Year’s events and after that increases gradually in the month after the events are over.
Yet, throughout the pandemic, this boost was postponed by numerous weeks.
CLICK ON THIS LINK TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
InFebruary and March 2020, NO2 levels over Wuhan and some other Chinese cities were well listed below long-lasting patterns. By April levels got better, reaching the long-lasting standard for the season.
That stated, NASA’s Earth Observatory kept in mind that increasing sunshine reduces the life time of the gas near the ground, and moving weather condition patterns can temper NO2 to distribute without resistance from the air.